Diamond Features
The following gives you an overview of the features of Diamond version 5. Please note that some functions will be (or have been)
released in minor updates 5.1, 5.2 etc. These minor updates may be free-of-charge for customers
of Diamond 5.x, see the Diamond Sales Page for details.
For a list of new functions and their (planned) releases, check the
"Function History" table.
Start the feature tour here - or directly step to the features you are interested
in via the links below.
>> Start feature tour >>
 |
Multiple structures, multiple pictures, many views
The Diamond document format enables storage of multiple structure data sets as well as multiple structure pictures. See the user interface elements that allow a better integration and correlation of the different views (the 3D structure picture edit view, thumbnails of the pictures in your document, several tables, powder pattern, etc.). Read about color coding of structural
parameter sets, the docking windows "More Pictures", "Recent Pictures" and "Undo
Buffer", the "Atom list" data pane, the table of created molecules,
and the possibility to view your structure picture in full screen view.
|
 |
Automatic and batch structure picture creation
See the "Auto Picture Creator" docking pane
that automatically applies changes in building options, picture design and viewing
direction directly to the structure picture, and the "design schemes"
that serve as a kind of style sheets that let you easily convert your structure
picture for presentation or publication.
|
 |
Structure picture display
About flat vs. rendering representation.
Ball-and-stick, wires, sticks, space-filling models, thermal ellipsoids, and many more.
Models can be assigned individually to selected atoms. So you can display ball-and-stick, space-filling, ellipsoid, and sticks or wires in one and the same picture.
Support for disorder parts, improved mixed sites representation.
|
 |
Manual building and designing of a picture
You can build up your structure picture from scratch, e.g. by filling a cell range or creating some initial atoms
of the parameter list that serve as starting points for completions of coordination spheres or molecules or so.
Or you start from one or more pictures that you have prepared using automatic or semi-automatic picture creation.
Nevertheless, you can individually build up or dismantle the structure framework step-by-step with a lot of
building and designing functions to give your picture the finishing touch.
|
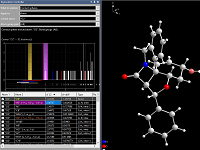 |
Exploration view
In this special view you can check and change the bonding spheres as well as spheres for non-bonding contacts and H-bonds
in a manner that is more interactive than just shifting sphere boundaries in distances histograms in the Connectivity and Atomic Environments dialog windows.
Most of the picture designing functions are not available in this view, so you can focus on the study of bonding and contact spheres.
|
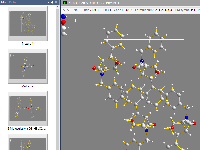 |
Productivity workflow
Read about two commands introduced in Diamond 5 to improve the work flow of creating pictures: Take picture and Continue with new picture.
This allows you to save impressions of your crystal or molecular structure spontaneously and use the dropped pictures as starting points
for more elaborated versions of structure pictures - or simply discard some, if you took too many pictures.
Read about special working modes in Diamond: the "Grab mode"
for more intuitive rotation, shifting or zooming during exploration of a crystal
or molecular structure, the "Neighbouring preview" of atoms and
molecules around the atom (bond, molecule) under mouse cursor, with several options
to use the mouse wheel to change properties (enlargement factor, zoom in/out, change
atom radii) or to change surroundings (blow up polyhedra, expand molecule cluster,
etc.) ("Mouse wheeling").
|
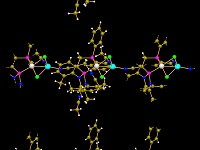 |
Functionality for molecules and polymers
Get an overview of the several options to create a packing diagram
(cell range, sphere, slab, or slice of molecules), about the support of non-bonding
contacts and the improved handling of H-bonds. And
there are several new functions to be applied on big molecules or organic and inorganic
polymers as well (expansion of molecular clusters, growing
or cutting of polymeric frameworks, pumping up of
inorganic frameworks).
|
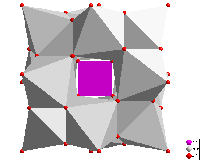 |
Polyhedron functions
The "Atomic environment" of an atom site each serves as an optional
criterion to define the coordination polyhedron's atoms (or a coordination sphere).
There are several functions to construct polyhedra with rather complicated geometry,
such as construction from atoms or bonds,
combination or splitting of polyhedron faces by clicking, copy and
paste of polyhedra between atoms of same site. And see how Voronoi
polyhedra are constructed.
|
 |
Calculate and measure distances, angles, planes, lines and more
Planes can be defined by hkl or as (best) plane through a set of three or
more atoms (or a line through two or more atoms). The planarity (linearity) can
be checked.
Besides this, distances of atoms from planes or lines as well as angles between
planes and/or lines can be calculated or measured interactively.
|
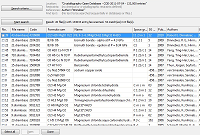 |
Searching for structure data
Read about access to the crystal structure database COD ("Crystallography Open Database") including
(amongst others)
AMCSD ("American Mineralogist Crystal Structure Database")
as well as CIF files from the
IUCr journals.
A small Structure Type Database is also available, where you can browse through
a list of the most common inorganic structure types and can load ready-to-use structure pictures.
|
 |
Create POV-Ray scenes
The POV-Ray assistant helps you to create photo-realistic pictures for this
outstanding, free available ray-tracer, with features like textures,
background, ray-tracing, multiple light sources, etc.
You can also create animated POV-Ray pictures or video sequences from POV-Ray pictures.
|
|

